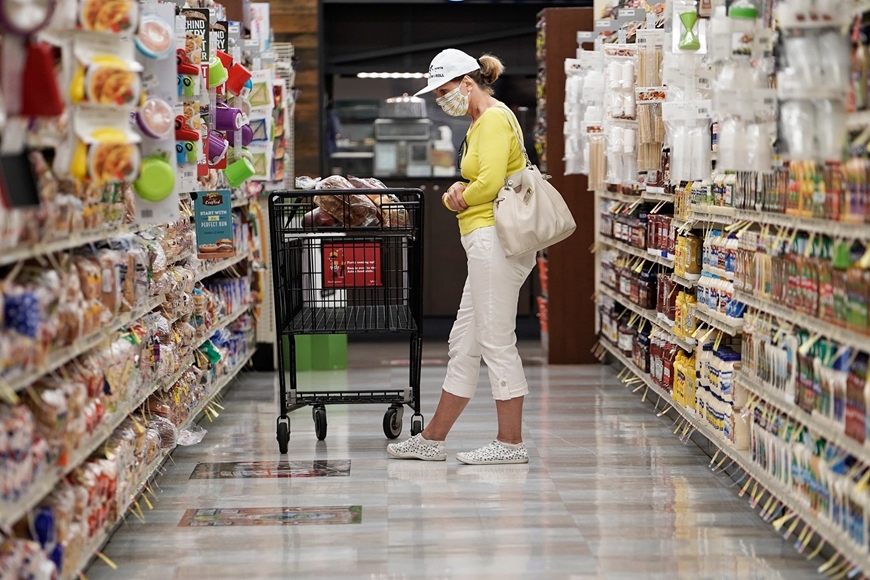
Yesterday (September 13), US stocks experienced the strongest sell-off since mid-2020. The Dow Jones fell nearly 4%, the S&P fell 4.32% and the Nasdaq index lost as much as 5.16 %.
Right after opening, the market was covered in red because of the surprising inflation report. Instead of cooling down as expected, the US inflation index in August still increased by 0.1% compared to the previous month. Lower gas prices did not help the index down.
From the beginning of the year until now, many economists as well as policy makers have said that food and fuel are the two biggest causes of high inflation in the US. Therefore, once the bottlenecks in the supply chain are removed and gas prices cool down, costs will drop, leading to lower price pressures in the entire economy.
However, the August inflation report poured cold water on this statement. The numbers suggest that inflation has spread to the entire economy, so it will last longer and be harder to deal with than anticipated.
Core inflation – the CPI that excludes two highly volatile commodities, food and fuel – rose 0.6 percent in August, more than double the Dow forecast. Jones. Compared to the same period last year, this index increased by 6.3%. If including food and energy, CPI increased by 0.1% month-on-month and 8.3% from 12 months ago.
More importantly, the source of inflation is no longer the price of gasoline, which fell 10.6% in August.
Far-reaching inflation
It’s not gasoline, but food, shelter and medical services are the causes of rising US inflation. This is bad for the lowest income segment of the economy and raises very important questions about the source of inflation.
“The core inflation numbers are hot. Prices for everything are up, from vehicles to healthcare and rent,” said Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics. “This is the most worrying point of the August inflation report.”
Prices for new cars and medical care both rose 0.8 percent in August. Accommodation costs – including rent and other home-related expenses – accounted for nearly a third of the basket. items that make up the CPI and increased by 0.7%.
The Home Food Price Index rose 13.5% year-on-year, the strongest since March 1979. Prices of items such as eggs and bread continue to soar, weighing heavily on household budgets.
For health services, the 0.8% increase was the strongest since October 2019. Veterinarian expenses increased by 0.9% month-on-month and over 10% year-over-year.
“Even things that normally go down in price like clothes increased slightly (about 0.2%). In my opinion, in the context of the current decline in oil prices, assuming the price of gasoline does not increase again, the US economy will still have widespread inflation although the level may decrease a bit in the future. ,” said Zandi. He forecast that inflation would not return to the Fed’s 2% target until early 2024.
The report also has some positive points, such as the price of airfare, coffee and fruit has decreased. Earlier this week, the New York Fed released survey results showing consumers are less concerned about inflation, although they still expect the rate of inflation to stay at 5.7% over the next year. There are also many signs of improvement across the supply chain.
Will oil prices rise again?
About three-quarters of commodities are still seeing price increases of more than 4% year-over-year, making the “temporary inflation” argument that the White House and the Fed are still trying to spread the word.
And no one can be sure energy prices will continue to stay at their current low levels.
The US and other G7 nations have said they intend to impose price controls on Russian oil starting December 5. This is likely to lead to retaliatory moves from Russia, causing oil prices to escalate in the last month of the year.
“If Moscow cuts off all oil and gas exports to the EU, US and UK, prices will return to peaks made in June. The average gas price could soon increase sharply from 3 .7 USD/gallon as it is now,” said Joseph Brusuelas, chief economist at RSM.
The expert added that even if the housing market is moving and the US economy falls into a recession, prices will not cool down anytime soon. House prices are lagged by a year or more.
In the context that inflation pressure is still very high today, the big question is how the Fed will adjust interest rates. Markets are betting the Fed will raise its benchmark interest rate by at least 0.75 percentage points after next week’s meeting.
“2% inflation represents stable prices. That’s the Fed’s goal. However, it is important for the Fed to find a way to achieve this goal without breaking everything. The Fed is not done yet. Going back to 2% is a very difficult journey. Overall, we see inflation has cooled down a bit, but should the Fed stop raising interest rates when inflation is at what level?”, Brusuelas said.
Check out CNBC
Source: Vietnam Insider