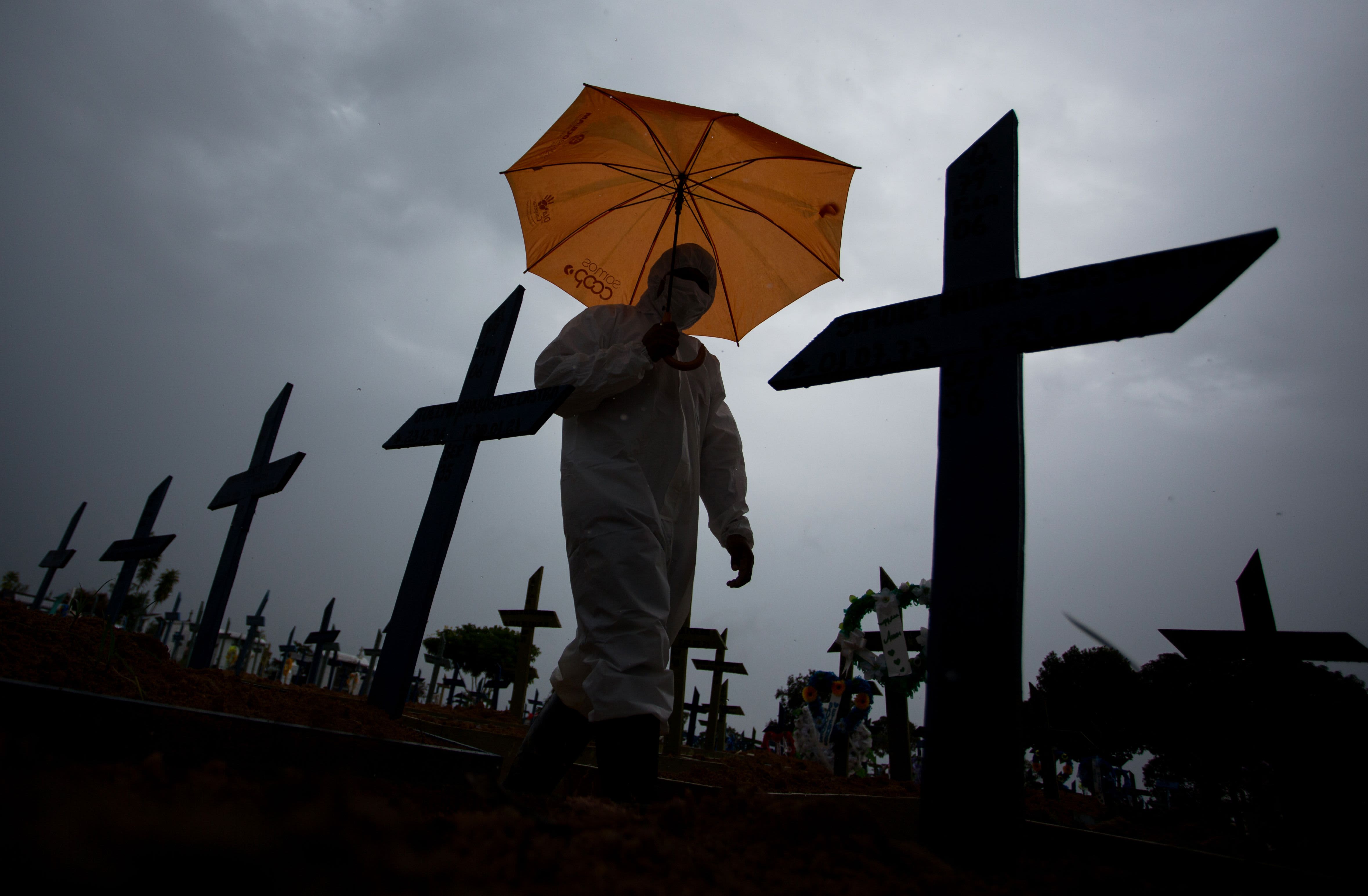
A worker wearing a protective suit and carrying an umbrella walks past the graves of Covid-19 victims at the Nossa Senhora Aparecida cemetery, in Manaus, Brazil, on February 25, 2021.
Michael Dantas | AFP | Getty Images
The global death toll from Covid-19 exceeded 4 million late Wednesday as infections worldwide crossed 185 million, according to data compiled by Johns Hopkins University.
Many countries have in recent months battled a surge in Covid infections due to the spread of a more transmissible delta variant, which first emerged in India. That comes more than a year since the World Health Organization declared the coronavirus outbreak a global pandemic.
The WHO has said that delta is the “fastest and fittest” variant yet, and health experts have warned that it could undermine efforts to contain the pandemic even as vaccination campaigns are underway.
“When it’s more transmissible, you get more cases. When you get more cases, you get more severe disease,” said Dale Fisher, a professor in infectious diseases at the National University of Singapore’s Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine.
Fisher told CNBC’s “Squawk Box Asia” that higher Covid transmission could lead to “more opportunity for new variants” that could be more transmissible than delta.
Vaccination against Covid-19 has started in many countries, with more than 3.3 billion doses administered globally, Hopkins data showed.
But high-income countries, which secured most of the early vaccine supplies, are far ahead most middle- and low-income nations in vaccinating their people.
Source: CNBC